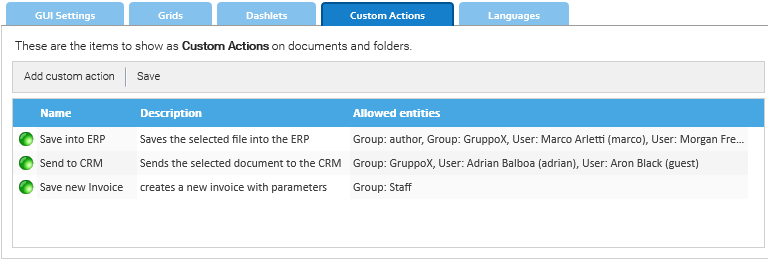
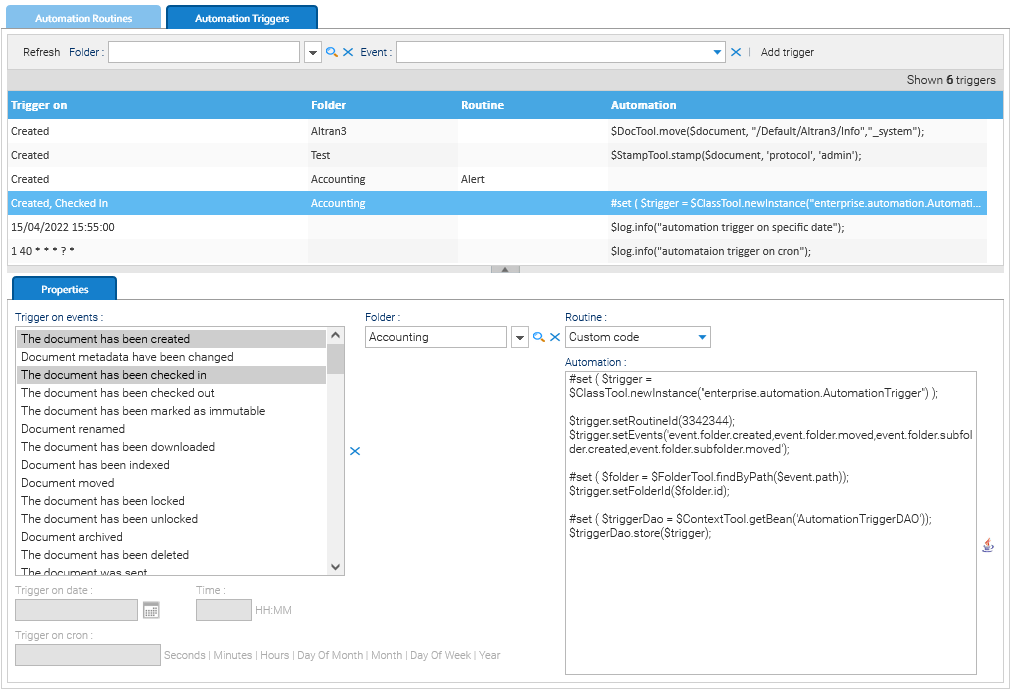
GUI Settings
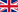
A set of behaviors and parameters of the user interface are configurable in the GUI Settings page.
- Welcome message: a message displayed to all the users when they sign in
- Preview window: percentage of the screen width occupied by the preview window
- Preview timeout: max. time to render the preview
- Thumbnail size: dimension of the thumbnails
- Thumbnail quality: quality of the thumbnails (100 is the best quality)
- Tile size: dimension of the tiles
- Tile quality: quality of the tiles (100 is the best quality)
- Thumbnail size for mobile: dimension of the thumbnails in the mobile app
- Thumbnail quality for mobile: quality of the thumbnails in the mobile app (100 is the best quality)
- Avatar size: pixels for the user's avatar
- Upload max. size: maximum allowed size for a single upload
- Disallowed ext.: list of file extensions that will not be accepted during the upload
- Text ext.: list of file extensions that can be edited with the embedded text editor
- Attribute text box width: size of the text boxes used to display and edit the extended attributes
- Attribute text area width: size of the text areas used to display and edit the extended attributes with Text Area input mode
- Attribute text area height: height of the text areas used to display and edit the extended attributes with Text Area input mode
- On double-click: what happens when a user double-clicks on a file
- Document Tab: what is the open tab when the user selects a file
- Folders sorting: folders sorting policy
- Folder pagination: if you want the folder's tree to handle pagination
- Folder page size:number of elements per page (if folder pagination is active)
- Show attributes of type Document as links: if the attributes that point to a document must appear as link
- Max. histories: number of elements in the history panel
- Security option: display the security options when a folder is created or copied
- Security option default: default policy for the security option when a new folder is created or copied
- Open folders tree: if the folders tree must be opened by default
- Open preview panel: if the preview panel must be opened by default
- Webstart mode: 'webstart' uses the client launcher, 'download' requires the user to download the .jar file manually
- Search hits: default number of hits returned by the search
- Web cont. Folders: list of folder ids that will be used by the web content editor to look for images and other contents
- Save login: if the user has the option to save his credentials in the browser
- Session timeout: if during this amount of minutes no interactions are received, the session will be closed
- RPC timeout: maximum time that the user interface waits for a response from the server
- Session heartbeat: frequency with which the interface attempts to contact the server
- Popup timeout: seconds the pop-up stays and displays a new message received
- Charset: default charset used to save some texts in the database (normally you use UTF-8 or US-ASCII)
- React to remote events: if the interface should process the remote events
- Show quota alerts in login: if you want to display an alert in the login screen when a quota has been reached
- Show license alerts in login: if you want to display an alert in the login screen when the support or license expiration is about to be reached
- Show update alerts in login: if you want to display an alert in the login screen when a new release is available
- Show patch alerts in login: if you want to display an alert in the login screen when an important patch has been released
- Alert server connection error: if you want to display an alert when the interface loses the connection to the server
- Save Input: Enable autocompletion on the attribute values
- Show language in login: if you want to display the language selector in the login screen
- Note max size: maximum size of the text of an annotation
- Email max size: maximum size of the body of an email
- Workflow dashlet rows: maximum number of rows displayed in the workflow dashlets
- Lock on editing: if the document must be immediately locked when the user starts to edit the metadata
Grids

In this section, you can configure the columns that will be displayed by default in the different grids of the interface. Each column represents an attribute of the document, and here you can choose the set of attributes you want and their order.
For each grid, you can also specify the maximum number of element displayed per page.
Dashlets
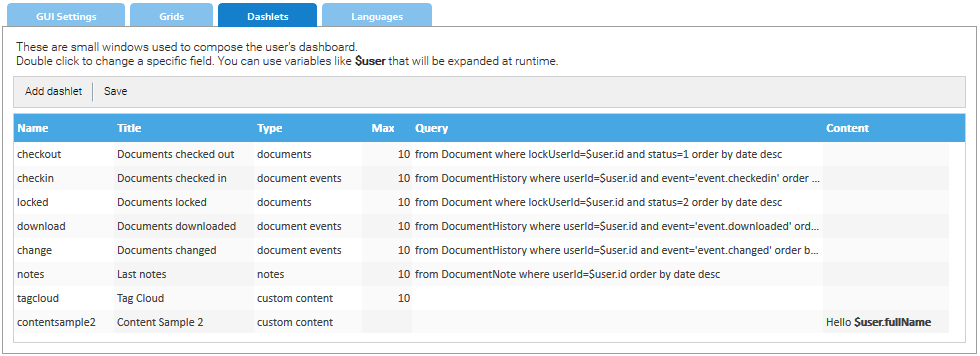
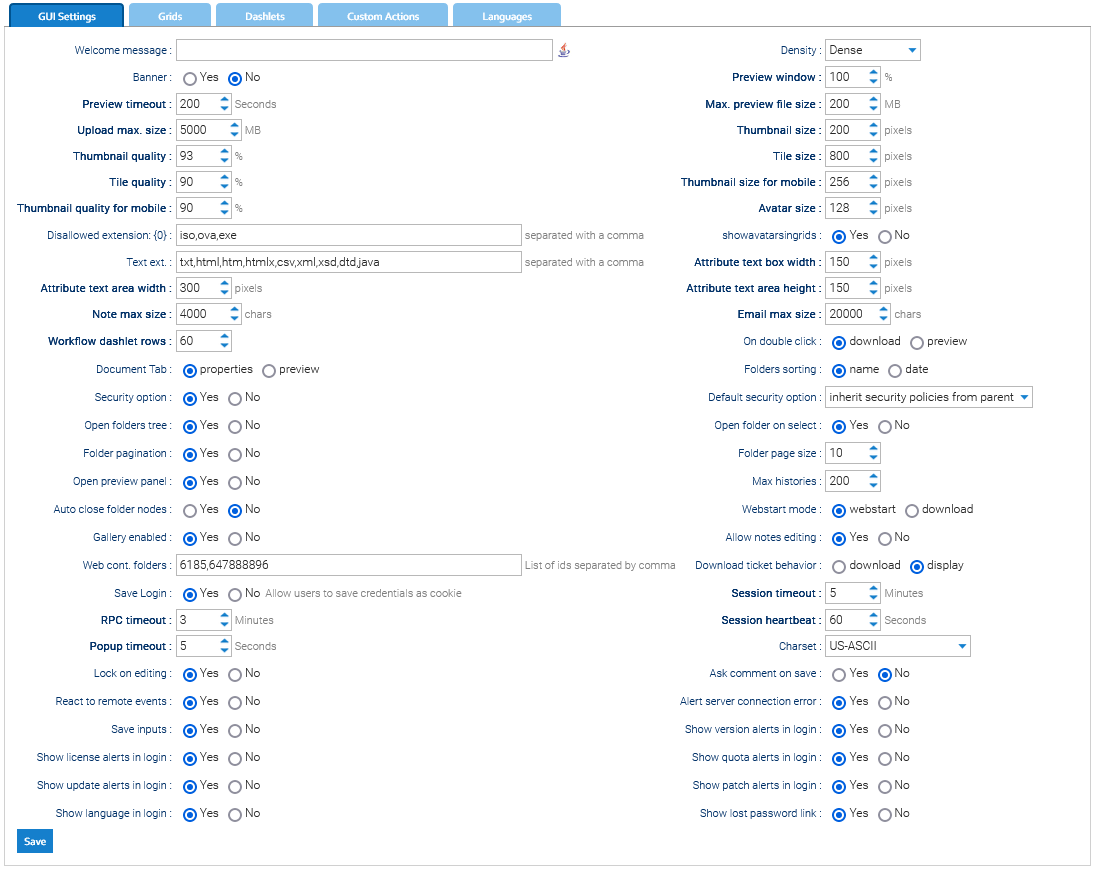
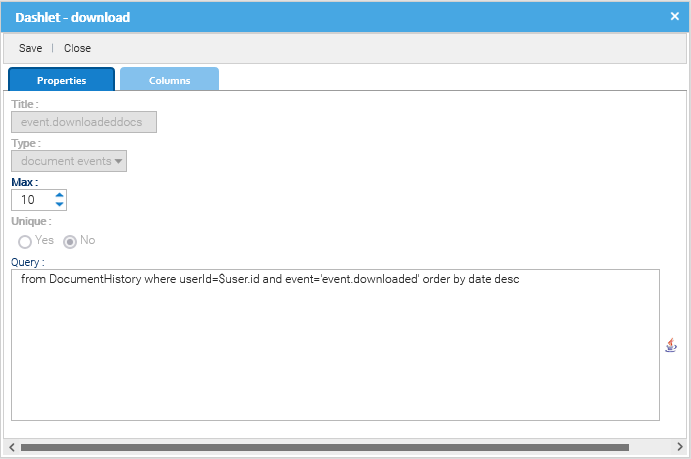
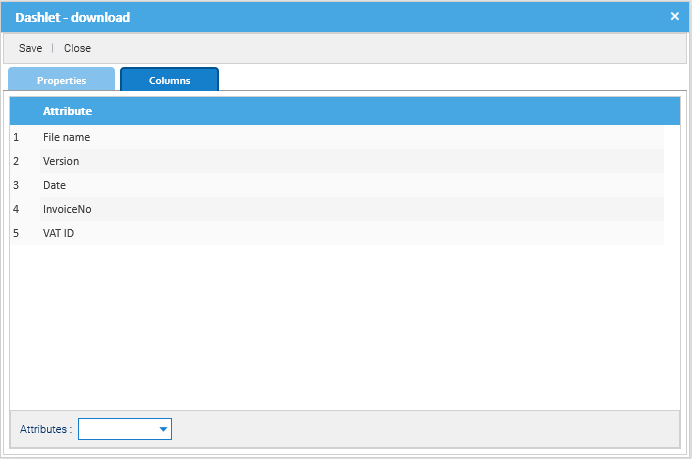
A dashlet is a small window that appears in the user's dashboard. The purpose of a dashlet is to show useful information about the user's activities inside the system. Read more.
Languages
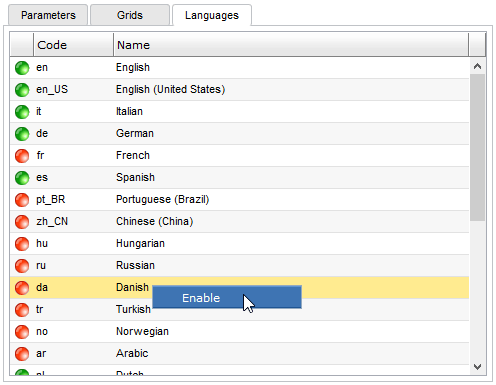
LogicalDOC supports a huge set of localizations, and in the Languages tab you can configure what languages you want to make available for the user interface.