Connetti la casella di posta elettronica di Google Gmail
LogicalDOC può connettersi a Gmail in due modi: utilizzando una password dell'app Google o utilizzando l'autenticazione OAuth 2.0. OAuth è il metodo consigliato e più sicuro, ma richiede una configurazione aggiuntiva in Google Cloud. Per una configurazione più semplice, puoi utilizzare una password dell'app, disponibile se il tuo account Google ha abilitato la verifica in due passaggi.
Connessione di LogicalDOC a Gmail tramite una password dell'app (App Password)
Per generare la password della tua app puoi seguire le istruzioni in questa pagina
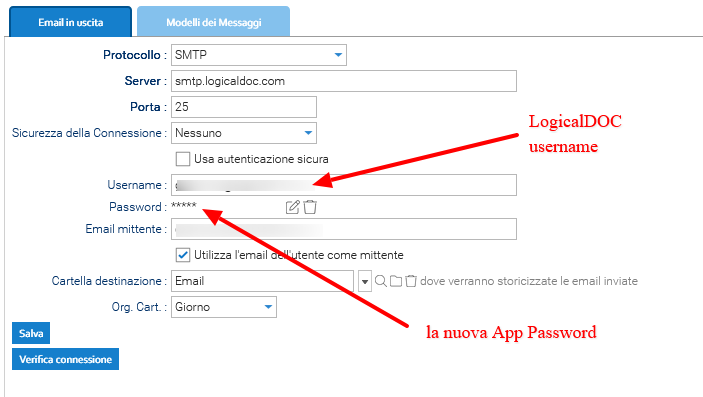
Una volta generata, inserisci la password dell'app in LogicalDOC semplicemente andando su Amministrazione > Importa ed esporta > Account Email
- Crea il nuovo account email da monitorare, cliccando su Aggiungi Account
- Nel campo Protocollo inserisci: IMAP o POP3
- Abilita SSL
- Nel campo Server inserisci: imap.gmail.com
- Nel campo Porta inserisci: 993
- Nel campo Nome utente inserisci la stessa casella di posta
- Nel campo Password inserisci la password dell'app creata (App Password)
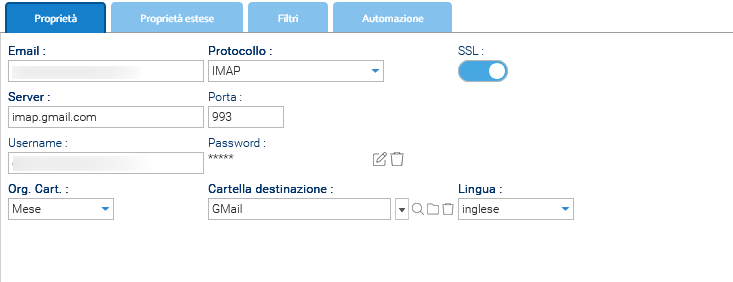
Salvare e testare la connessione della casella di posta.
Connessione di LogicalDOC a Gmail tramite OAuth
OAuth offre un metodo di autenticazione più sicuro e moderno per connettere LogicalDOC a Gmail senza memorizzare la password. Per configurarlo, puoi seguire le istruzioni riportate in questa pagina.
- Crea il nuovo account email da monitorare in Amministrazione > Importa ed esporta > Account email
- Nel campo Protocollo inserisci: IMAP Google o POP3 Google
- Abilita SSL
- Nel campo Server inserisci: imap.gmail.com
- Nel campo Porta inserisci: 993
- Nel campo Nome utente inserisci la stessa casella di posta
- Nel campo Password inserisci la password della casella di posta
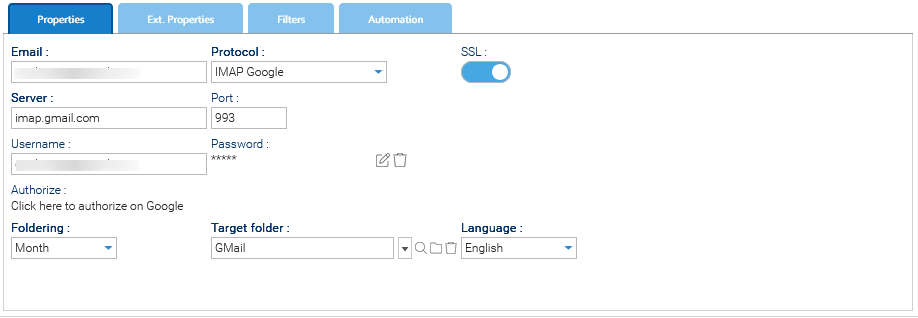
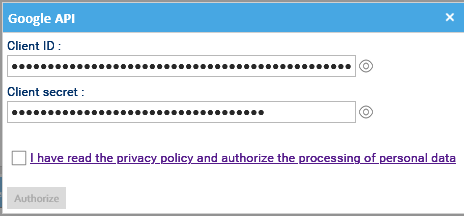
- Una volta impostato tutto, devi cliccare sul link Autorizza per inserire il Client ID e il Client Secret