Two Factors Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is now recommended to secure login to Internet services and protect against phishing attacks and credential theft. This authentication generates two-step verification codes for the users on their devices, thereby increases the security of your account by requiring a second verification step at the time of access.
Two-factor authentication makes it difficult for hackers to access online accounts and a person’s devices because of its advanced security level. It isn’t sufficient to recognize the victim's password to pass authentication verification. To prevent the data of their users’ from hackers, online services are progressively introducing 2FA. Two-factor authentication is responsible for accessing and controlling the sensitive data and systems.
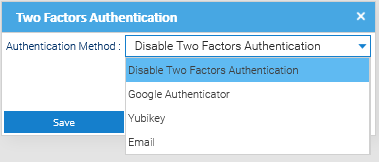
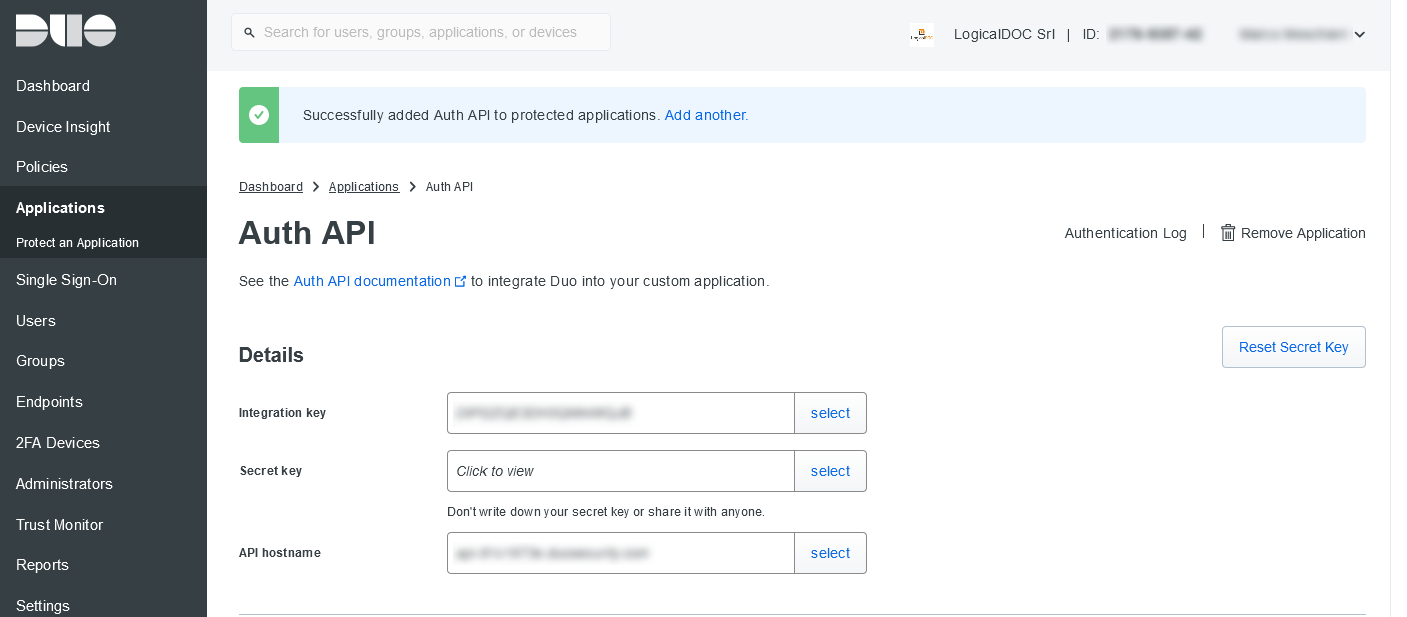
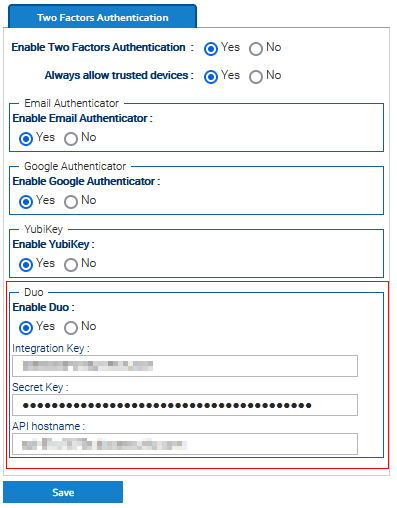
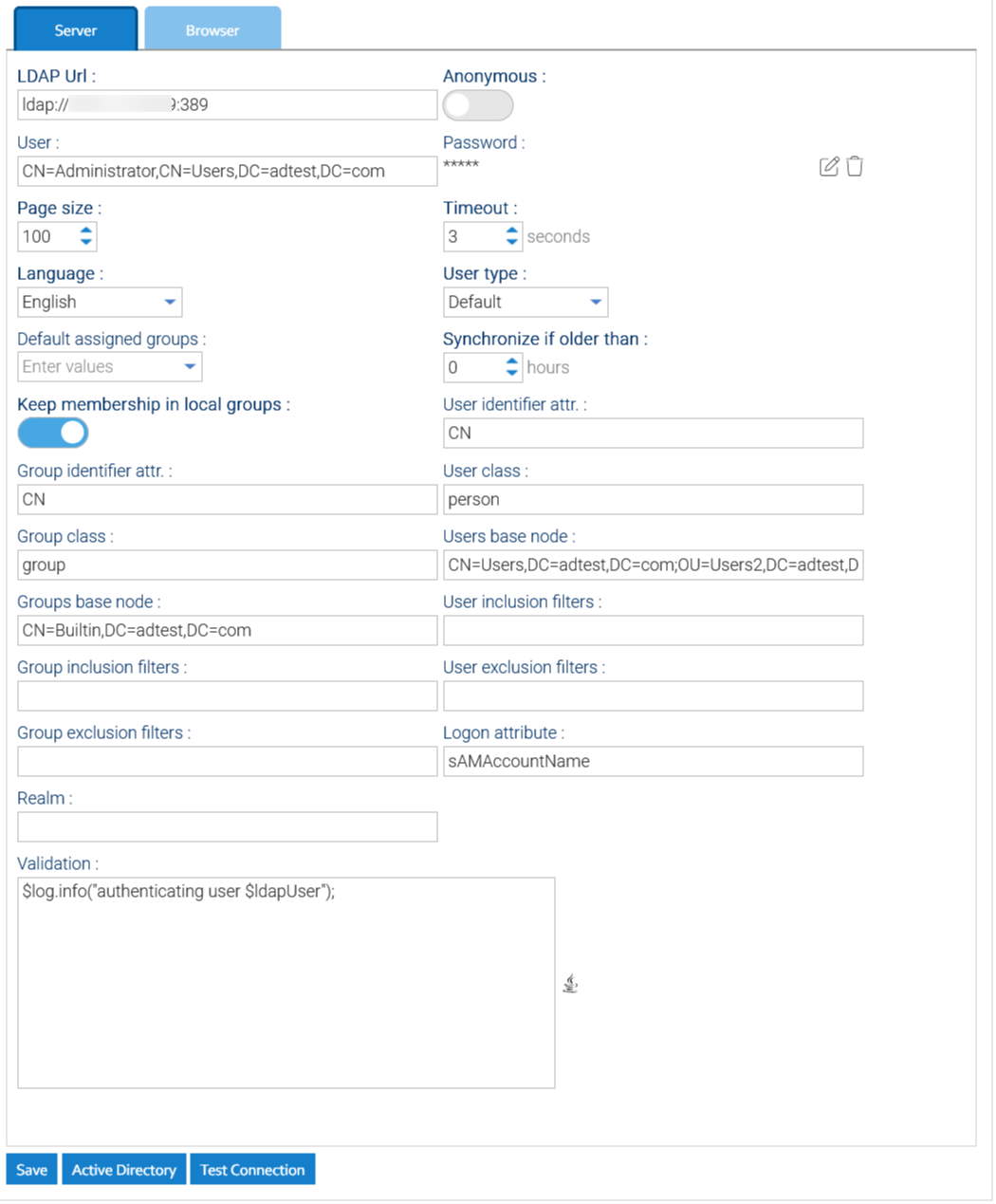
LogicalDOC supports the two-factor authentication integrating the most commonly uses 2FA technologies like Goole Authenticator, Yubikey or Duo.
Once the two-factor authentication is enabled, after filling the credentials a second login panel may appear asking to input the second factor key:
1
 |
2
 |
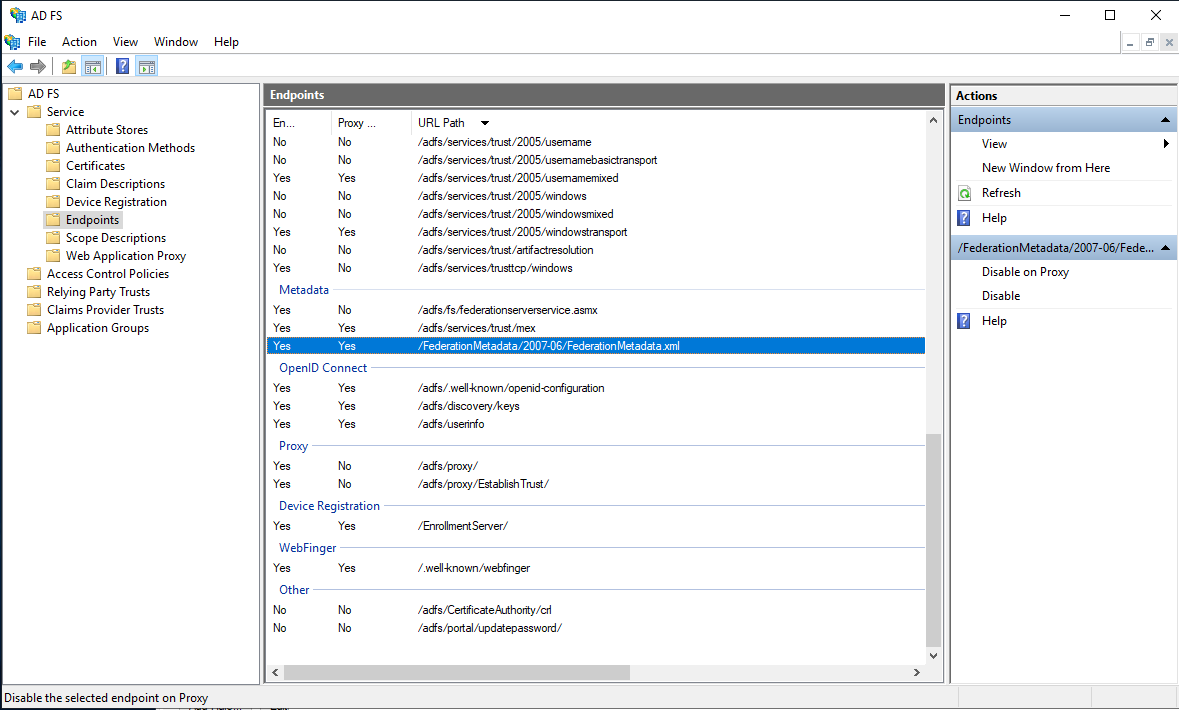
Enable this feature in Administration > Security > Two Factors Authentication, and also enable the authenticators you want to support.
Once this has been done, each user can enable the 2FA by using the menu Account > Security > Two Factors Authentication.
In any case, the administrator can force the 2FA on specific users. To do so, enter Administration > Security > Users and right-click on a user, then choose Two Factors Authentication.
In the popup, choose an authenticator and follow the indications. Please note that in general, the authenticators require the physical presence of the authentication device.